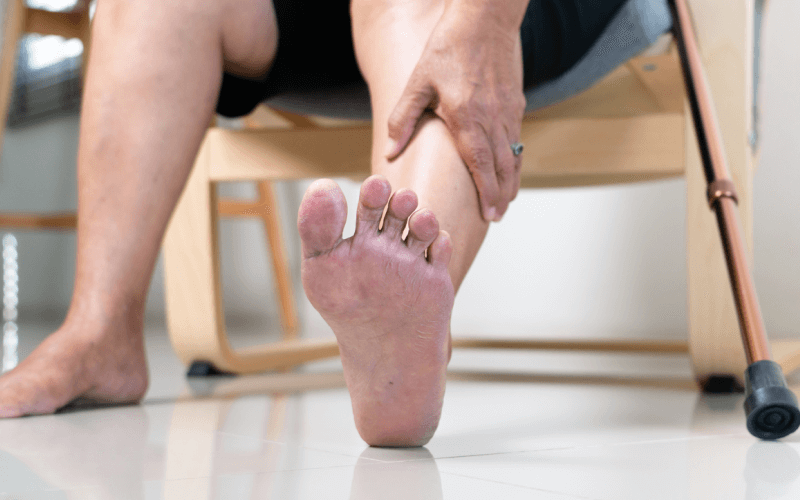
Could Your Itchy Feet be a Sign of a Bigger Health Issue?
Itching is a common sensation that can occur in different parts of the body, including the feet. Itchy feet can be caused by various factors, such as normal sweating, dry skin, or tight shoes. However, in some cases, itchy feet can be a sign of an underlying health condition that requires medical attention.
In this guide, we will discuss the skin-related and non-skin related health issues that can cause itchy feet, when to see a doctor, and how to prevent and manage it.

How Itchy Feet can be a sign of something more?
Itchy feet can be a sign of an underlying health condition that requires medical attention. The cause of this condition can be either skin-related or non-skin related. Skin-related causes include athlete’s foot, eczema, psoriasis, contact dermatitis, scabies, and fungal infections.
Non-skin related causes include diabetes, kidney disease, liver disease, allergies, pregnancy, thyroid problems, and neuropathic itch. Paying attention to it and identifying the underlying cause is important to avoid potential complications and to receive appropriate treatment.
How different people experience
Itchy feet can be experienced differently by different people. Some people may experience a mild itch, while others may have a more severe and persistent itch. The location and timing of the itch can also vary from person to person. Some people may experience this condition only at night, while others may have it throughout the day.
Over the counter medication for itchy feet
Over-the-counter medications, such as antifungal creams and corticosteroid creams, can provide relief for itchy feet. However, it is important to identify the underlying cause before using any medication. If the cause is unknown, it is recommended to seek medical advice before using any over-the-counter medication.
Skin related health issues that can cause itchy feet
Athlete’s Foot
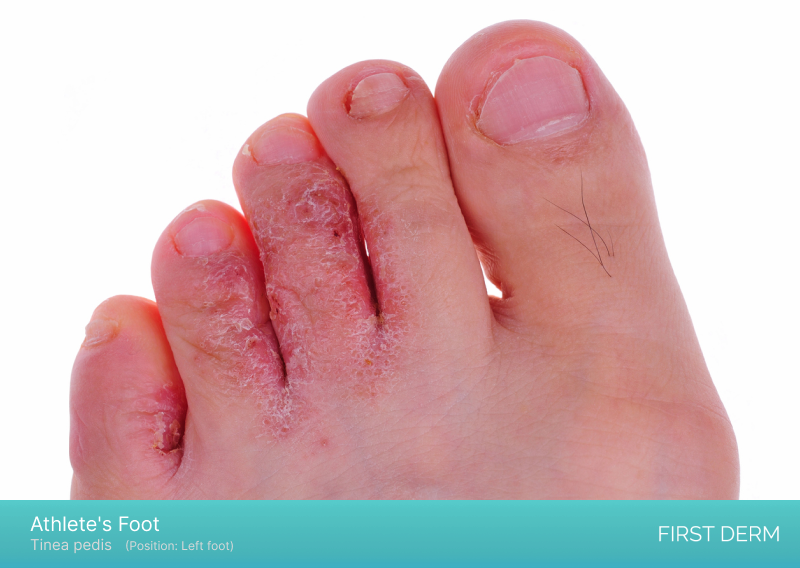
Close-up photograph of a foot with Athlete’s Foot, showing red, inflamed and scaly skin between the toes. Some blisters and peeling skin can also be seen, indicating a common fungal infection of the skin that causes discomfort and itchiness
Athlete’s foot, also known as tinea pedis, is a fungal infection that affects the skin on the feet. It is a common cause of itchy feet, especially in athletes and people who sweat a lot. This condition is highly contagious and can spread from person to person. The fungus thrives in warm and moist environments, such as locker rooms, public showers, and swimming pools.
Symptoms of Athlete’s foot include itching, burning, and stinging between the toes, as well as redness, scaling, and blisters. In severe cases, the skin may crack and peel, leading to secondary bacterial infections. Treatment for Athlete’s foot typically involves antifungal medications, such as creams, powders, and sprays, as well as measures to keep the feet dry and clean.
Eczema
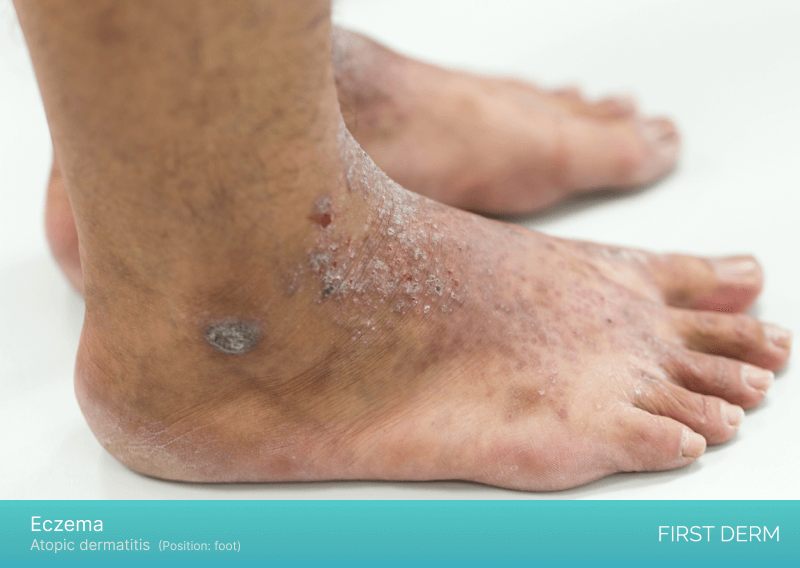
An image of atopic dermatitis on a person’s foot, showing red, itchy, inflamed patches of skin with areas of dryness, scaling, and possible oozing or crusting
Eczema, also known as atopic dermatitis, is a chronic skin condition that causes inflammation and itching. It is most common in children but can occur at any age. Eczema can affect various parts of the body, including the feet. The symptoms of eczema on the feet include redness, itching, dryness, and thickened skin. In severe cases, eczema can cause painful cracks and blisters.
The exact cause of eczema is unknown, but it is thought to be related to an overactive immune system and a genetic predisposition. Treatment for eczema typically involves corticosteroid creams, antihistamines, and moisturizers. In some cases, phototherapy or systemic medications may be necessary.
Psoriasis
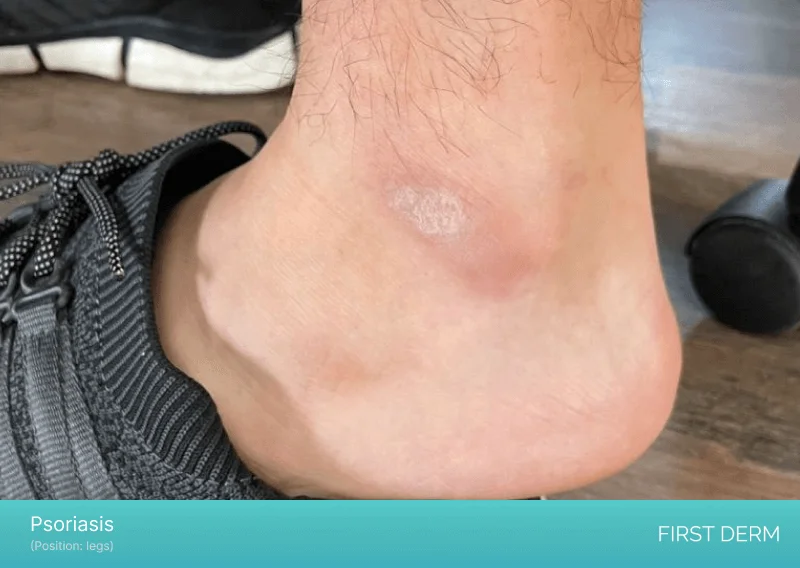
A photograph showing a light red patch on the ankle with white scales in the middle
Psoriasis is a chronic autoimmune disorder that affects the skin, nails, and joints. It causes the skin cells to grow too quickly, resulting in thick, scaly patches that are often itchy and painful. Psoriasis can affect any part of the body, including the feet. The symptoms of psoriasis on the feet include redness, scaling, and pitting of the nails.
Psoriasis is thought to be caused by a combination of genetic and environmental factors. Treatment for psoriasis typically involves topical medications, such as corticosteroids and vitamin D analogues, as well as systemic medications, such as methotrexate and biologic agents.
Palmoplantar pustulosis (PPP)
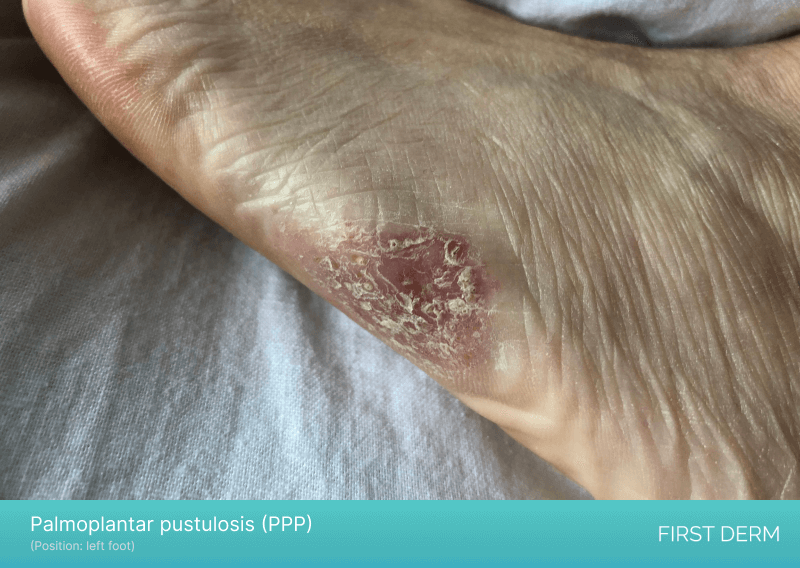
An image of Palmoplantar pustulosis (PPP) on a person’s foot, displaying raised, pus-filled bumps and patches of red, inflamed skin on the side of the foot, characteristic of this chronic and debilitating skin condition
Palmoplantar pustulosis (PPP) is not the same as psoriasis, but it is considered a subtype of psoriasis and may have similar symptoms. PPP is a chronic inflammatory condition that primarily affects the palms of the hands and soles of the feet. It is characterized by the presence of pustules or blisters that can be painful and cause significant discomfort.
In some cases, itchy feet may be a sign of PPP, which is often accompanied by thickening and scaling of the affected skin. PPP is thought to be caused by a combination of genetic and environmental factors, and it can be triggered or exacerbated by factors such as stress, smoking, and exposure to certain chemicals.
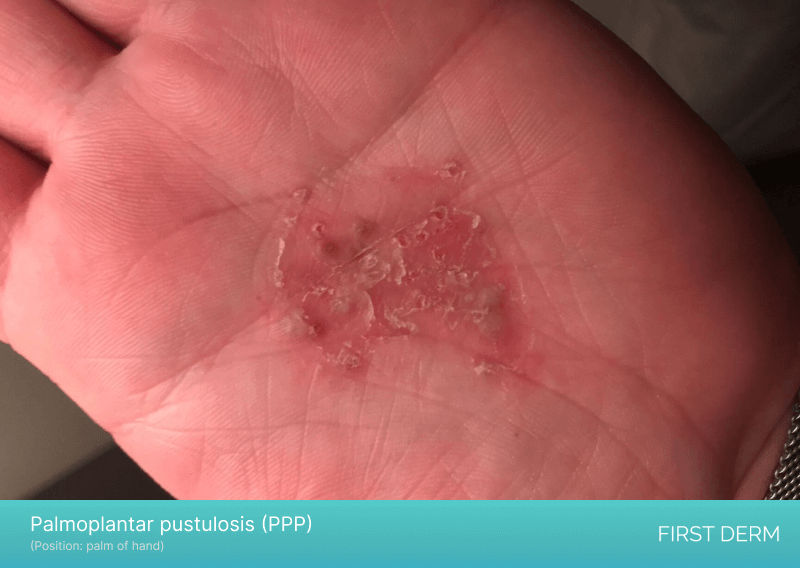
An image of Palmoplantar pustulosis (PPP) on a person’s palm, showing raised, pus-filled bumps and patches of red, inflamed skin on the palm, characteristic of this chronic and debilitating skin condition
Treatment for PPP may include topical medications, such as corticosteroids, as well as phototherapy and systemic medications. It is important to seek medical attention if you are experiencing persistent itching or discomfort in your feet, as this may be a sign of a bigger health issue such as PPP or another condition that requires proper diagnosis and treatment.
Contact Dermatitis
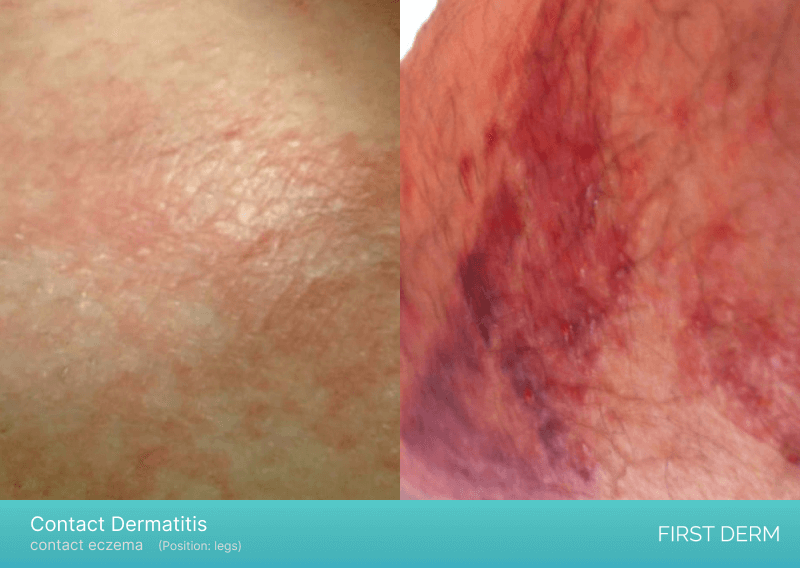
Contact dermatitis on a person’s leg, with two distinct forms shown in one image. The photo on the left displays irritative eczema with slight reddishness, while the photo on the right showcases red spots caused by plant contact
Contact dermatitis is a skin condition that occurs when the skin comes into contact with an irritant or allergen. The symptoms of contact dermatitis on the feet include redness, itching, and blisters. Common irritants and allergens include soaps, detergents, metals, and plants.
Treatment for contact dermatitis typically involves avoiding the offending substance and using topical corticosteroids and antihistamines to reduce inflammation and itching.
Scabies
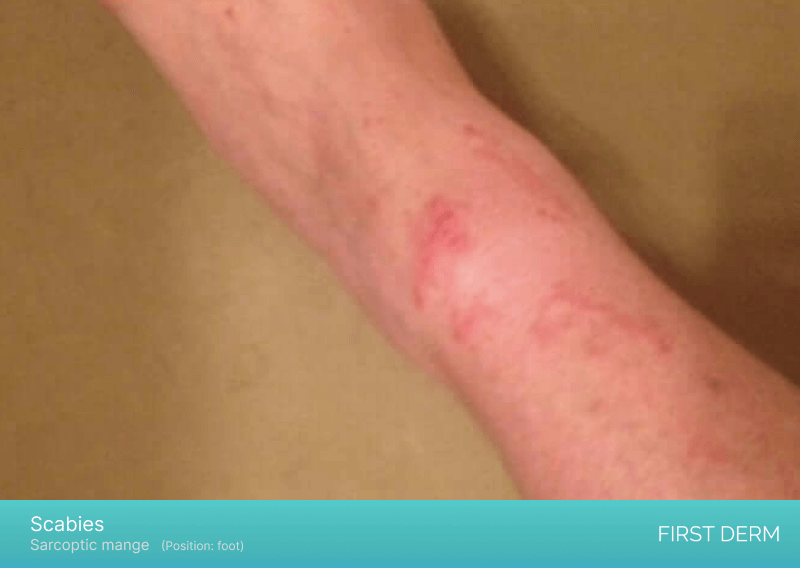
An image of scabies on a person’s foot, showing a close-up view of small, raised bumps and linear burrows in the skin, along with redness and itching
Scabies is a highly contagious skin condition that is caused by a mite that burrows into the skin. It is characterized by intense itching, especially at night. Scabies can affect any part of the body, including the feet. The symptoms of scabies on the feet include a rash, bumps, and blisters.
Treatment for scabies typically involves prescription medications, such as topical creams and oral medications, that kill the mites and their eggs are borrowed in the skin (causing the itching).
Fungal Infections
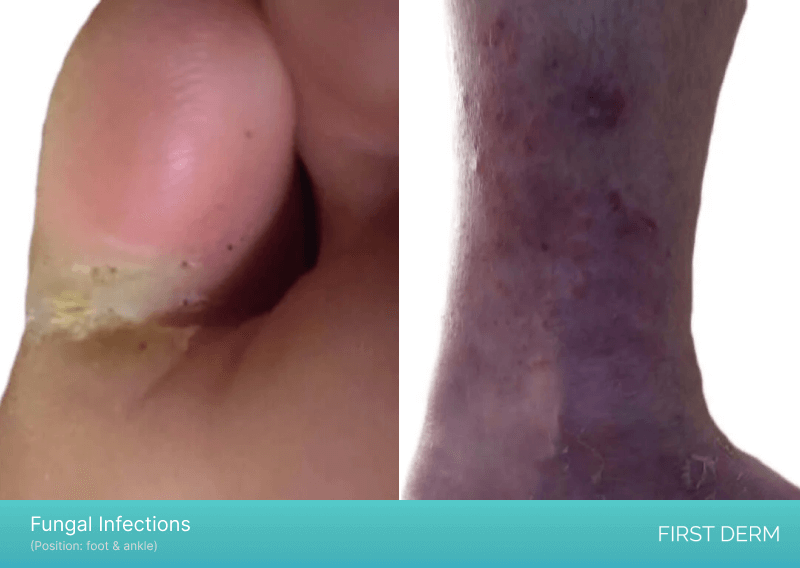
An image of a fungal infection on a person’s foot, showcasing two areas of infection. The photo on the left displays a fungal infection beneath the small toe, with a yellow color and small black spots on the affected skin. The photo on the right showcases a fungal infection closer to the ankle, showing redness, scaling, and possible blistering or cracking of the skin, typical of this common type of skin infection
Fungal infections, such as ringworm and candidiasis, can affect the skin on the feet and cause itching. Fungal infections thrive in warm, moist environments, such as sweaty shoes and socks. The symptoms of fungal infections on the feet include itching, redness, scaling, and blisters.
Treatment for fungal infections typically involves antifungal medications, such as creams, powders, and oral medications. In severe cases, nail removal or laser therapy
Non-Skin Related Health Issues
Diabetes
Diabetes is a condition that affects the body’s ability to produce or use insulin effectively, which can result in high blood sugar levels. It can also cause damage to the nerves in the feet, known as diabetic neuropathy. This can lead to a loss of sensation or a tingling sensation in the feet, as well as itching.
According to a study published in the journal Frontiers in Medicine, itchy feet are a common symptom among people with diabetes. The study found that nearly half of the participants with diabetes experienced foot itching. The study also found that participants with higher HbA1c levels (a marker of blood sugar control) were more likely to report itching.
Treatment for itchy feet caused by diabetes typically involves managing blood sugar levels and addressing any underlying nerve damage. Medications such as antihistamines or topical creams may also provide relief.
Kidney Disease
The kidneys are responsible for filtering waste and excess fluid from the blood. When they don’t function correctly, waste builds up in the body, leading to various complications, including itchy feet. It’s a common symptom of chronic kidney disease (CKD). A study published in the Journal of Renal Nutrition found that itch is a prevalent symptom among patients with CKD, affecting approximately 50% of patients.
The study identified several factors that may contribute to the development of itchy feet in patients with CKD, including inflammation, neuropathy, and mineral and electrolyte abnormalities.
Liver Disease
Liver disease can cause a range of symptoms, including itchy skin and itchy feet. This type of itching is thought to be related to the buildup of bile acids in the body, which can lead to irritation of the skin.
According to a review published in the Journal of Clinical and Translational Hepatology, itching is a common symptom among people with liver disease. The review found that up to 70% of people with cholestatic liver disease (a type of liver disease that affects the flow of bile) experience itching.
Treatment for itchy feet caused by liver disease depends on the underlying condition. In some cases, medications such as antihistamines or bile acid sequestrants may provide relief. However, in more severe cases, medications that target the underlying liver disease may be necessary.
Allergies
Allergies can cause a variety of symptoms, including itchy skin, hives, and swelling. Allergic reactions can also cause itchy feet. Common allergens that can cause itchy feet include latex, detergents, soaps, and certain foods. In some cases, allergies can also cause contact dermatitis, a type of skin inflammation that causes itchy, red, and swollen skin. According to a study published in the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology, contact dermatitis is a common cause of foot itch, affecting up to 10% of the general population.
Pregnancy
Pregnancy can cause several changes in the body, including changes in hormone levels, blood volume, and immune function. These changes can lead to various complications, including itchy feet. According to a study published in the Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology Research, pruritus is a common symptom during pregnancy, affecting approximately 20% of pregnant women.
The study found that the severity of pruritus is positively correlated with the duration of pregnancy. Itchy feet during pregnancy can be caused by several factors, including hormonal changes, cholestasis of pregnancy, and pregnancy-induced eczema.
Thyroid Problems
The thyroid gland produces hormones that regulate several bodily functions, including metabolism, heart rate, and body temperature. When the thyroid gland doesn’t function correctly, it can lead to several complications, including itchy feet. Hypothyroidism, or an underactive thyroid gland, can cause dry skin and itchiness. According to a study published in the Indian Journal of Dermatology, dry skin and pruritus are common symptoms of hypothyroidism, affecting up to 15% of patients.
Neuropathic Itch
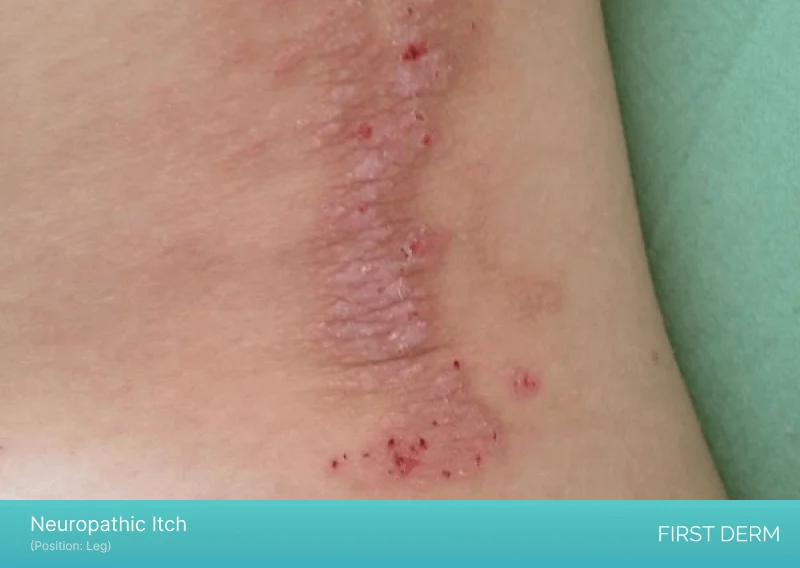
Close-up image of a leg with Neuropathic Itch, showing red, inflamed skin
Neuropathic itch is caused by damage or dysfunction of the nerves that transmit sensations to the brain. In some cases, this type of itch may be accompanied by a burning or tingling sensation. It is often difficult to diagnose and treat, but it can be associated with conditions such as diabetes, kidney disease, and liver disease. According to a study published in the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology, neuropathic itch has been reported in up to 20% of patients with chronic kidney disease.
When it comes to treatment, neuropathic itch can be challenging to manage. Topical treatments such as creams or ointments may not be effective, and oral medications used for other types of itching may not work for neuropathic itch. However, antihistamines, antidepressants, and anticonvulsants have been used with some success. In some cases, treating the underlying condition may also help alleviate neuropathic itch.
When to See a Doctor
This condition can sometimes be a sign of a bigger health issue, and it’s important to know when to seek medical attention. Some warning signs and symptoms that warrant a visit to the doctor include:
- Severe itching that does not go away with over-the-counter treatments
- Redness, swelling, or warmth around the affected area
- Blisters or open sores on the feet
- Pain or discomfort in the feet
- Foul odor or discharge from the affected area
- Itching that spreads to other parts of the body
- Fever or chills
If you experience any of these symptoms, it’s important to make an appointment with your dermatologist. They can perform diagnostic tests to determine the underlying cause of your itchy feet and develop a treatment plan that’s tailored to your needs.
Diagnostic tests for itchy feet may include a skin biopsy, blood tests, or allergy tests. Your doctor may also ask you questions about your medical history and any medications you’re taking.
Treatment Options
Treatment for itchy feet will depend on the underlying cause of the condition. For skin-related causes, your doctor may prescribe topical creams, ointments, or oral medications to help alleviate symptoms and clear up any infections or inflammations. For example, antifungal medications may be prescribed for athlete’s foot or fungal infections, while topical steroids may be recommended for eczema or psoriasis.
If your itchy feet are caused by a non-skin related health issue, your doctor may recommend treatments to address the underlying condition. For example, if you have diabetes, proper management of blood sugar levels can help alleviate symptoms of itchy feet. Similarly, if you have liver disease, treatment may involve medications or lifestyle changes to manage the condition.
In some cases, your doctor may also recommend lifestyle changes to help prevent or manage itchy feet. For example, if you have allergies, avoiding triggers may help alleviate symptoms. If you’re pregnant, wearing comfortable shoes and elevating your feet may help reduce swelling and discomfort.
More than 70% of our users get better with Over-the-Counter Medication
Avoid an unnecessary visit to a doctor! Receive expert dermatological advice from the comfort of your own home.
Key takeaway
Itchy feet can be a nuisance, but they can also be a sign of a bigger health issue. By understanding the causes and warning signs of itchy feet, you can take steps to monitor and address your foot health.
If you’re experiencing severe or persistent itching, redness, or swelling, it’s important to seek medical attention. Your doctor can perform diagnostic tests to determine the underlying cause of your symptoms and develop a treatment plan that’s tailored to your needs.
By practicing good foot hygiene and making certain lifestyle changes, you can also help prevent itchy feet and keep your feet healthy and comfortable. Remember to pay attention to your feet, and don’t hesitate to seek medical attention if you have concerns about their health.
Disclaimer
The information provided in this content is for educational and informational purposes only and is not intended as a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the advice of your physician or other qualified health provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition.
References:
- Joly P. Itching: how and why?. European journal of dermatology : EJD. 2015;25(1):2-4. doi:10.1684/ejd.2014.2472. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25565463
- Oiso N, Fukai K, Kawada A. Itch in Atopic Dermatitis: Pathophysiology and Treatment. Allergology international : official journal of the Japanese Society of Allergology. 2019;68(1):8-12. doi:10.1016/j.alit.2018.07.003. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6315576/
- Bergasa NV. Pruritus in Patients with Liver Disease. World Journal of Gastroenterology. 2009;15(21):2654-2659. doi:10.3748/wjg.15.2654. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2777587/
- American Diabetes Association. (n.d.). Diabetes & Foot Problems. Retrieved March 2, 2023, from https://www.diabetes.org/diabetes/complications/foot-complications
- National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke. (2021, November 10). Neuropathic itch. Retrieved March 2, 2023, from https://www.ninds.nih.gov/Disorders/All-Disorders/Neuropathic-Itch-Information-Page
- Office on Women’s Health. (2019). Pregnancy and itching skin. Retrieved from https://www.womenshealth.gov/pregnancy/youre-pregnant-now-what/pregnancy-and-itching-skin
- Public Health England. (2016). The green book, chapter 15: Hepatitis B. Retrieved from https://www.gov.uk/government/publications/hepatitis-b-the-green-book-chapter-18
- University of Wisconsin-Madison Health. (2021). Pruritus (itching). Retrieved from https://www.uwhealth.org/health-topic/pruritus-itching/4945
Ask a Dermatologist Now
Anonymous, fast and secure!

The Specialist doctor from the University Hospital in Gothenburg, alumnus UC Berkeley. My doctoral dissertation is about Digital Health and I have published 5 scientific articles in teledermatology and artificial intelligence and others.