Hives (Urticaria)
Medically reviewed by The Dermatologists and written by Dr. Alexander Börve
Hives also known as urticaria, are itchy bumps on the skin that may occur within minutes of a triggering event.
The rash normally disappears within hours to a maximum of a couple of weeks. For chronic hives, itches and rashes can usually remain for at least two months, possibly longer. The first sign is the itch, and then the rash.
There are many different causes that triggers the rash, including infection, hypersensitivity to certain medications or certain foods, insect bite, cold, heat, pressure, or contact with toxic substances in certain plants.
Try our FREE dermatology search engine and get peace of mind within a second
Symptoms
They appear as one or more raised rashes, as the release of the substance histamine in the skin causes local inflammation (swelling, itching, redness). It varies in shape, from a small single rash to a large contiguous area and can change quickly in appearance, location without leaving any marks when they disappear. In rare cases, they turn into a serious allergic reaction, but it usually resolves itself.
They can have many different causes, including infection, hypersensitivity to certain medications or certain foods, stress, insect bite, cold, heat, pressure, or contact with toxic substances in certain plants. In many cases, the cause of the rash in adults remains unclear, despite investigation.
Demographism
When you scratch the skin lightly, a red or white line will appear, and it will remain for about an hour. Do not scratch or rub the skin and do not use close-fitting clothes, as this may worsen the condition.
Effort or cholinergic urticaria
Urticaria can occur when body temperature increases during physical exertion, fever, hot baths or stress. The susceptibility to this type of rash typically persists for a few years and then disappears.
Cold-triggered urticaria
This type of hives is triggered by cold and windy weather and is often located to the face and hands, which may swell and turn red. If symptoms arise, do not drink ice-cold water, do not eat cold items and do not bathe in cold water.
Light-triggered urticaria
Light-triggered urticaria occurs primarily in ages 20-40. A few minutes of exposure to sunlight can make the skin itchy and red. Light sensitivity can be associated with certain drugs. A test of sensitivity to UV light can provide valuable information.
Pressure-triggered urticaria
This urticaria mainly appears on hands, feet, and sitting muscles.
In Children
In childhood, hives are usually triggered by an infection (viruses, streptococci, glandular fever) or some foods such as eggs, nuts, fish, and flour. Hives on adult can be triggered by drugs such as: penicillin, sulfur, aspirin, codeine, B vitamins, or X-ray contrast. The following food-substances have been known to trigger a reaction: strawberries, shellfish, tuna, blue cheese, nuts, soy, kiwi, and a combination of seafood and wine.
Try our FREE dermatology search engine and get peace of mind within a second
What can I do?
To relieve the symptoms you can shower in cool water or lubricate the affected area with ointments, such as calamine lotion. To reduce itching, you can try prescription pills that contain antihistamine. However, you should not give antihistamines to children under six years without consulting your doctor first. Both calamine lotion and antihistamines can be bought in pharmacies. Investigate what triggers the hives.
Try our FREE dermatology search engine and get peace of mind within a second
Should I seek medical care?
Contact your healthcare provider if the itch is too disturbing or the rash remains after a week. Urticaria can be signs of inflammatory connective tissue diseases (collagenosis) or a type of cancer called paraneoplastic phenomena.
You should also seek help if you get hives more than once or if you suspect you are allergic. In rare cases, hives become an allergic shock. Then, your lips and tongue can go numb, or your face can turn red. You may have itching that often begins on the scalp and then spreads to the face, nose and tongue. You can also have severe itching on the palms and soles of the feet. If you get the above symptoms, you should call for an ambulance or immediately seek help at a hospital. The situation can become worse if you do not receive treatment immediately.
They can be associated with lip swelling and throat itchiness and shortness of breath, which is a medical emergency called angioedema. Call for immediate medical help for any swelling of the airway.
Try our FREE dermatology search engine and get peace of mind within a second
Treatment
Antihistamines treat against itching. If simple antihistamines do not work, seek a medical attention. Once you’ve got hives, you are extra sensitive to substances that can further irritate the skin. The sensitivity usually lasts at least one week. During that time you may want to avoid eating certain foods, such as shellfish, tuna and strawberries. Otherwise, it may break out again. For the same reason, you should also be cautious with alcohol for about a week after you have had hives.
Source:
American College of Allergy, Asthma and Immunology. Hives (Urticaria). Available at: https://acaai.org/allergies/types/skin-allergies/hives-urticaria
American Academy of Dermatology. Hives. Available at https://www.aad.org/public/diseases/itchy-skin/hives
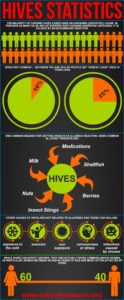
Are Hives Contagious. Infograph Showing Hives Statistics. Available at https://arehivescontagious.wordpress.com/2015/04/04/infograph-showing-hives-statistics/
Ask a Dermatologist
Anonymous, fast and secure!

The Specialist doctor from the University Hospital in Gothenburg, alumnus UC Berkeley. My doctoral dissertation is about Digital Health and I have published 5 scientific articles in teledermatology and artificial intelligence and others.
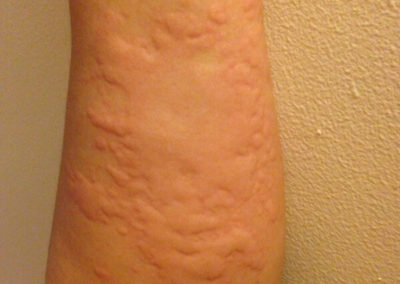
![Hives (Urticaria) (01) leg [ICD-10 L50]](https://www.firstderm.com/wp-content/uploads/Hives-Urticaria-01-skin-ICD-10-L50-400x284.jpg)
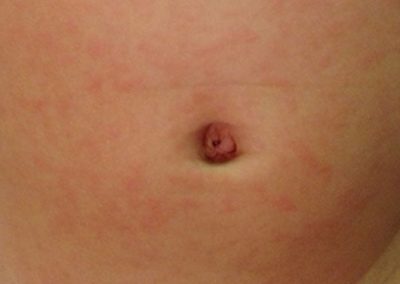
![Hives (Urticaria) (17) skin [ICD-10 L50]](https://www.firstderm.com/wp-content/uploads/Hives-Urticaria-17-skin-ICD-10-L50-e1592936953496-400x284.jpg)