Abscess
Medically reviewed by The Dermatologists and written by Dr. Alexander Börve
Common
- Self-diagnosable
- Symptoms: Firm bump with the middle filled with pus and debris
- Color: Typically red
- Location: Commonly found in armpits, around the anus and vagina, near your tailbone, around a tooth and in the groin region
- Treatment: Warm compression, antibiotics, incision and drainage, surgery
Skin abscesses, also called boils, are collections of pus in the skin. Abscess are caused by an inflammatory response from your body’s defenses. It is triggered when your immune system tries to kill germs that get under the skin or in the oil (sebaceous) glands.
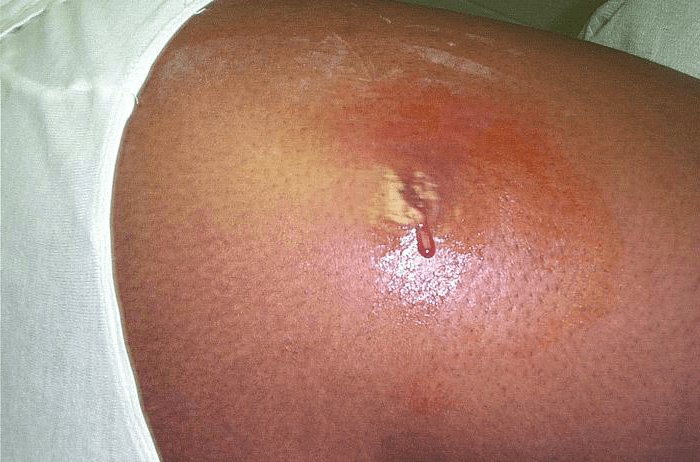
Skin Abscess on the Arm: A 1cm wide inflamed area with a pus-filled center, indicative of infection and immune response, seen in medium brown skin
When the body’s immune system begins to fight off the infection, white blood cells move through the walls of the blood vessels into the area of the infection and collect in the damaged tissue. Thus, the boil becomes filled with pus. The collection of pus includes dead cells, bacteria, and debris. This process then expands and inflames the surrounding follicles and tissue, causing pain. People with weakened immune systems are more prone to getting abscesses. Boils themselves are not contagious, but the bacteria that cause them are.
Symptoms
A tender mass that is usually surrounded by pink or red discoloration of the skin.
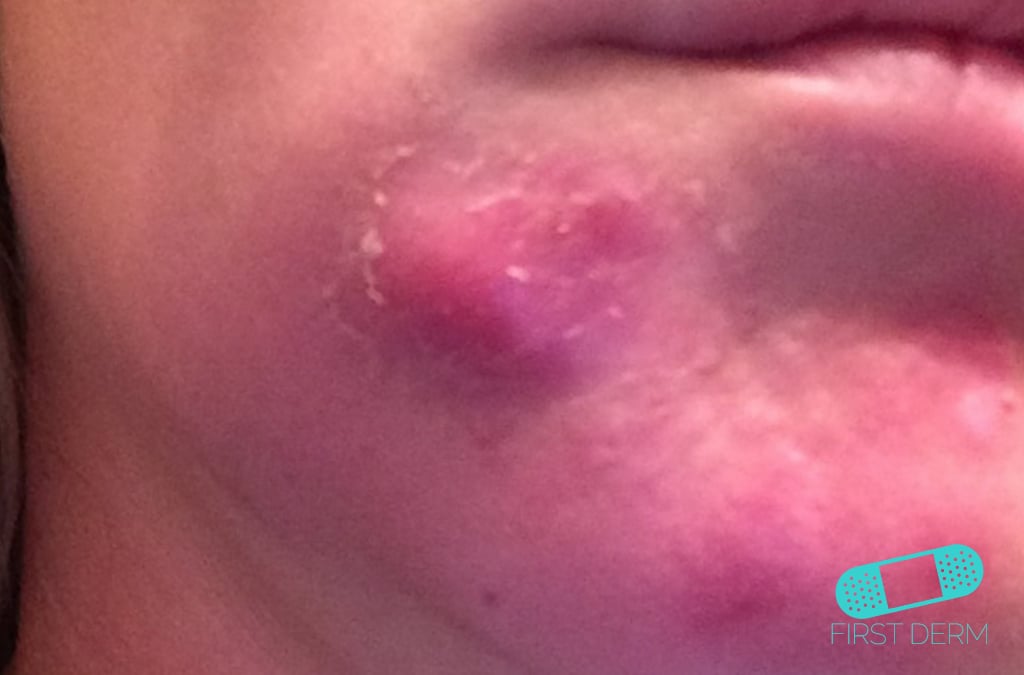
Cheek abscess on a person, appears as a swollen, reddened area closer to the lower lips
The middle is filled with pus and debris. It causes a firm reddened bump that may increase in size. Boils are painful to touch and can appear anywhere on your body.
They are most commonly found in armpits, around the anus and vagina, near your tailbone, around a tooth and in the groin region. Areas around hair follicles can be inflamed and aggravate the development.
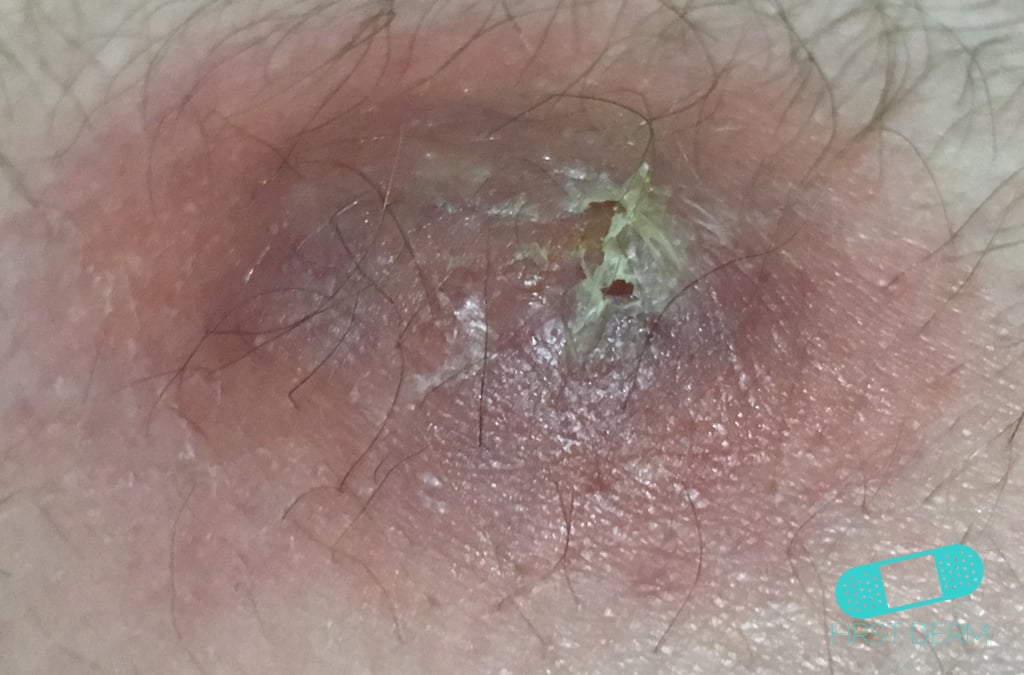
Scalp Abscess: A Distinct Swollen, Reddish Area Signifying Inflammation and Infection
Causes of Skin Abscesses
Typically, skin abscesses develop due to bacterial entry into the skin, often through minor cuts or near hair follicles.
While it’s common to have bacteria on the skin, their entry into the skin can lead to pus formation and abscesses.
Risk Factors
- Smoking
- Obesity
- Diabetes
- Age: Particularly common in ages 15 to 40.
- Skin Conditions: Eczema and similar issues heighten susceptibility
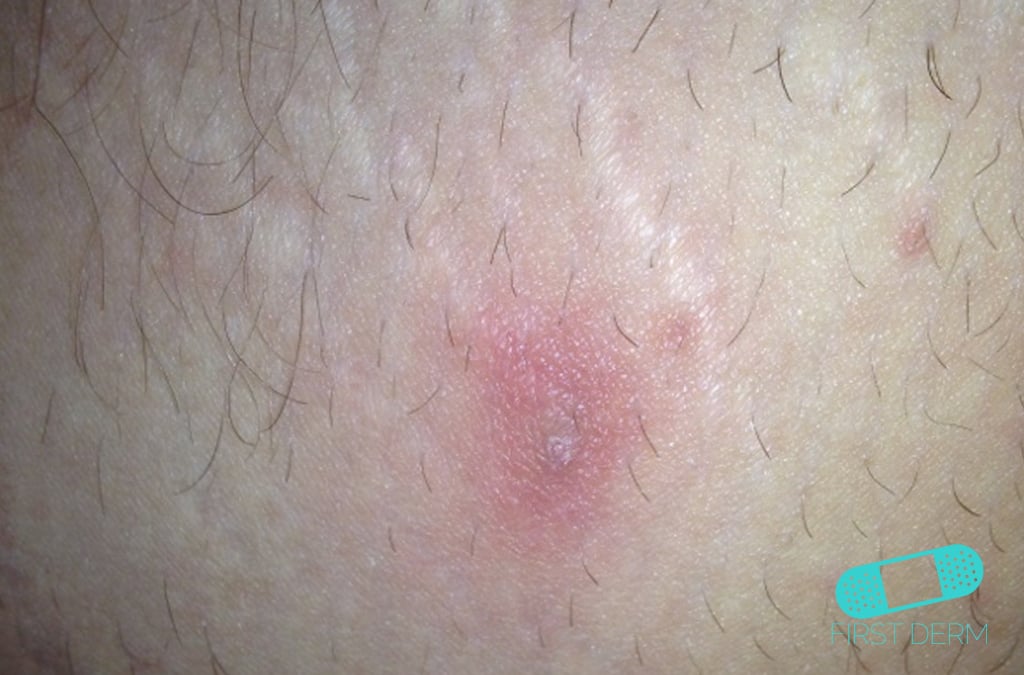
Waist Abscess: Swollen, Reddish Area with a Central Point, Highlighting Inflammation Without Visible Pus
What can I do?
Good hygiene can prevent skin boils. For small ones of half an inch or less, you may drain them naturally. You can apply a warm compress to the area for up to 30 minutes to help relieve some pain. The warmth may help reduce swelling and speed up healing. Do not attempt to drain by pressing on the infection as this can push the infection into other tissues. Whatever is used for compression should be washed thoroughly as well, in order to prevent the infection from spreading.
Should I seek medical care?
Self-treatment alone may be inadequate in treating boils. It is imperative to get treatment early, as most will not improve unless you seek care as the infection can spread and lead to a fever. It will likely have to be opened and drained by a doctor through a process called incision and drainage in order to improve recovery.
See a doctor if the boil:
- Is a lump that is getting bigger.
- Lasts more than 2 weeks.
- Is hard and does not move.
- Is a lump or swelling in your breast.
- Occurs and you have a weakened immune system or a long-term condition like diabetes.
Treatment
Antibiotics For larger ones, your doctor may prescribe antibiotics to clear the infection. This course of medication works against a wide range of known infectious bacterias. Otherwise, the doctor will take a sample of fluid from the abscess and test it. This is to identify the type of germ that causes the condition and prescribe more specific antibiotics. It is important to take a swab and send it to the labs before taking the antibiotics, so to secure the pathogen causing the infection.
Incision and drainage Some requires draining. The small surgery is usually performed under a local anesthetic. The surgeon will make a cut to remove the pus and clean the hole with sterile saline. The procedure may leave a small scar.
Surgery If your internal boil is too large to be drained with a needle, if a needle cannot get to the infection safely, or if needle drainage has not been effective in removing all of the pus, you may need to undergo surgery.
Last updated on November 20, 2023
Source
- Treatment of Skin Abscesses: A Review of Wound Packing and Post-Procedural Antibiotics. Mark List, Donella Headlee, Katherine Kondratuk. S D Med. 2016 Mar;69(3):113-9.
- Subramaniam S, Bober J, Chao J, Zehtabchi S. Point-of-care Ultrasound for Diagnosis of Abscess in Skin and Soft Tissue Infections. Acad Emerg Med. 2016;23(11):1298-1306. doi:10.1111/acem.13049
- Skin Abscess. NHS UK. Last reviewed June 2, 2023. Accessed November 17, 2023. https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/skin-abscess/
- Bowman JK. Abscess Incision and Drainage. Prim Care. 2022;49(1):39-45. doi:10.1016/j.pop.2021.10.002
- MedlinePlus [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Library of Medicine (US); Abscess; [cited 2023 Nov 20]; [about 2 p.]. Available from: https://medlineplus.gov/abscess.html.
Ask a Dermatologist
Anonymous, fast and secure!

The Specialist doctor from the University Hospital in Gothenburg, alumnus UC Berkeley. My doctoral dissertation is about Digital Health and I have published 5 scientific articles in teledermatology and artificial intelligence and others.