Vitamin D supplements and reduced skin cancer risk
Skin cancer is an ever-growing global epidemic with an increasing number of individuals being diagnosed each year, with over 5 million cases diagnosed each year in the United States alone. It is a type of malignancy caused by mutations to skin cell DNA due to exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun.
Though most skin cancers can be effectively treated when detected early, prevention of skin cancer is still vital to reduce the burden of this disease. While prevention efforts have typically focused on minimizing exposure to UV radiation, there is growing evidence that vitamin D, which is produced in the skin when exposed to UV radiation, may also play a role in reducing the risk of skin cancer. Lately, regular usage of vitamin D for skin cancer has emerged out as an important topic in the field of dermatology. In this article, we will review the current research on the relationship between vitamin D and skin cancer, and discuss the potential mechanisms by which vitamin D may help to prevent & reduce the risk of skin cancer.
Latest research
- A latest research conducted by dermatologists found that people who regularly take vitamin D supplementation are at a lower risk for skin cancer, as opposed to those who do not consume the supplement.
- A recent research study observes a key finding that people who take vitamin D supplements were less likely to have melanoma, which is a form of skin cancer, compared to those who did not take supplements.
- This finding also suggests that even occasional users of vitamin D may have a lower risk for melanoma than non users.
“Whatsoever, the question about the optimal dose of oral vitamin D inorder for it to have beneficial effects to prevent or treat melanoma still remain unanswered. Until we know more, national intake recommendations should be followed.”
Ilkka Harvima (Professor of Dermatology and Allergology)
This cross-sectional study was conducted under the North Savo Skin Cancer Programme and the patients were recruited at the dermatological outpatient clinic of Kuopio University Hospital. Medical history and examination of patients were carefully analyzed by experienced dermatologists at the University of Eastern Finland.
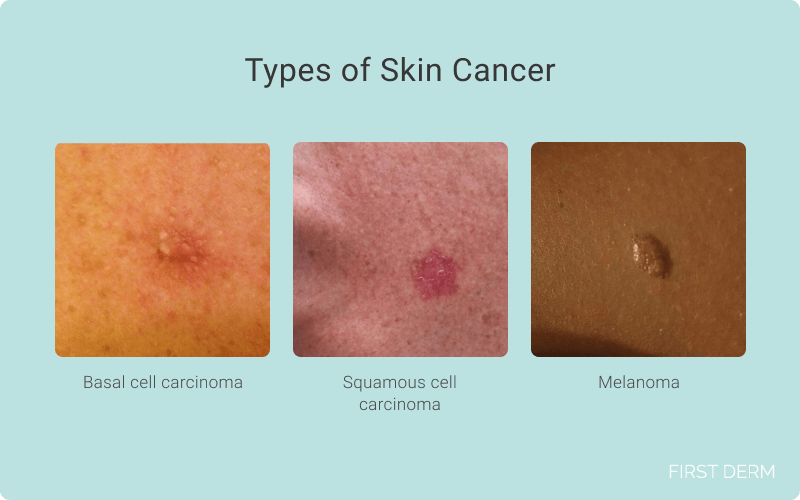
The research involved 498 adult patients with an estimated high risk of skin cancer including basal cell carcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma and melanoma.
Skin cancer: a run-through
Skin cancer is a severe medical condition that can lead to severe consequences if not treated promptly. The disease occurs when the DNA in skin cells is harmed, often by being exposed to UV radiation from sources such as tanning beds or the sun. There are three main types of skin cancer: basal cell carcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma, and melanoma.
To protect your skin from the sun’s harmful rays, it’s crucial to wear protective clothing, use sunscreen, avoid prolonged exposure to direct sunlight during peak hours (usually between 10 a.m. and 4 p.m.), and seek shade. It’s also important to conduct regular self-examinations of your skin and be alert to any changes, such as the appearance of new moles or growths, changes in the size or color of existing moles, or any sores that don’t heal. If you notice any of these changes, you should seek medical attention immediately.
Vitamin D: An overview
Vitamin D is often referred to as the “sunshine vitamin” because it is produced in the skin in response to sunlight exposure. When ultraviolet B (UVB) rays from the sun come into contact with the skin, a form of cholesterol in the skin called 7-dehydrocholesterol is converted into vitamin D3.
Vitamin D plays an important role in maintaining healthy skin. It helps to regulate the growth and differentiation of skin cells, and it can also help to reduce inflammation and promote wound healing. Vitamin D may also help to prevent skin aging by reducing the breakdown of collagen and elastin in the skin.
However, it is important to balance the benefits of vitamin D with the potential risks of sun exposure, such as skin damage and skin cancer. It is recommended to get vitamin D through a combination of sun exposure (in a safe and responsible manner), diet, and supplements, and to protect the skin with sunscreen and other protective measures when spending time outdoors.
Sources of vitamin D
- Synthesized in the skin which is induced by sun exposure
When your skin is exposed to the sun, it has the ability to create vitamin D on its own. According to Dr. David J.Leffell, a dermatologist at Yale Medicine and the head of Dermatologic Surgery, our bodies contain cells that have vitamin D receptors, and when these cells are exposed to ultraviolet B (UVB) from the sun, they go through a series of reactions that begin with the conversion of cholesterol in the skin and ultimately result in the production of vitamin D3.
- Through diet
There are limited natural food options that are rich in vitamin D. The top food sources of vitamin D include oily fish like salmon, tuna, and mackerel, along with egg yolks and mushrooms. Additionally, some foods such as milk, orange juice, and certain breakfast cereals are artificially enriched with vitamin D.
Meeting the recommended daily intake of vitamin D solely through diet can be difficult, especially for people who follow a vegan or vegetarian diet.
- Vitamin D supplements
Vitamin D supplements are available in different forms, such as tablets, capsules, and drops, and can be bought over the counter from health food stores, pharmacies, and online retailers. It’s essential to choose high-quality supplements that have been independently tested for quality and purity. Some supplements may also contain additional ingredients like calcium or magnesium that can aid in bone health. It’s important to choose the right dose of vitamin D based on individual factors such as age and sex.
To improve absorption, it’s recommended to take vitamin D supplements with a meal. Before taking any new supplement, it’s essential to read and follow the instructions on the supplement label and consult with a healthcare professional. Although vitamin D supplements can help boost vitamin D levels in the body, it’s still important to get enough sun exposure and consume a balanced diet that contains vitamin D-rich foods like fortified dairy products and fatty fish.
Importance of Vitamin D for skin health
Vitamin D is essential for maintaining healthy skin. Here are some key reasons why:
- Promotes skin cell growth and repair: Vitamin D helps promote the growth and repair of skin cells, which is crucial for maintaining healthy skin. It also helps regulate the production of skin cells, which helps maintain the proper balance between cell growth and death.
- Helps prevent skin aging: Vitamin D has been shown to help prevent premature aging of the skin by reducing oxidative stress and inflammation. This can help keep your skin looking young and healthy.
- Supports the skin’s immune system: Vitamin D is important for supporting the skin’s immune system, which helps protect against infections and other skin problems.
- Reduces the risk of skin cancer: Adequate levels of vitamin D may help reduce the risk of skin cancer, especially in people who are exposed to high levels of sunlight.
- Helps maintain skin barrier function: Vitamin D helps maintain the skin’s barrier function, which is important for preventing moisture loss and protecting against environmental stressors like pollution and harsh weather.
In summary, vitamin D is important for maintaining healthy skin by promoting cell growth and repair, preventing premature aging, supporting the skin’s immune system, reducing the risk of skin cancer, and maintaining the skin’s barrier function.
Interconnection between vitamin D and risk of skin cancer
In the recent Melanoma research , 498 individuals aged 21 to 79 years, including 253 males and 245 females, were categorized into three groups based on their intake of vitamin D supplements: non-use, occasional use, or regular use.
The researchers aimed to determine whether regular vitamin D supplementation led to higher levels of serum calcidiol, which is the storage form of vitamin D in the body, and has been linked to cancer risk in some studies.
According to the findings, individuals who took vitamin D supplements regularly had higher levels of serum calcidiol compared to those who did not use supplements. This suggests that there is a correlation between vitamin D supplements and the risk of skin cancer, and that consistent use of these supplements may potentially decrease the risk of developing skin cancer.
Vitamin D supplementation
There have been various studies investigating the potential relationship between vitamin D supplementation and the risk of melanoma, a type of skin cancer. While some studies have indicated that higher vitamin D levels could reduce the risk of melanoma, others have shown no significant association or even a possible increased risk.
25(OH)D is the main circulating form of vitamin D that is used to assess whether a patient is vitamin D deficient, sufficient or intoxicated. It represents the level of both vitamin D intake and vitamin D that is produced in the body from sun exposure.
Vitamin D status of an individual may vary with a number of factors.
“Since natural vitamin D is produced by the skin in response to sunlight, reducing exposure to UV radiation to avoid cancer reduces the amount of naturally produced vitamin D in the body, potentially leading to the need for supplementation” explained medical oncologist Dr. Kim Margolin.
According to his statement, an individual’s vitamin D status may depend on other factors in addition to UV exposure. They are;
- Age
- Skin color
- Body weight
- Genetics
- Geographic location
- Dietary intake
- Air pollutants
- Pregnancy
- Certain medical conditions
Dr. Margolin further stated that the harmful impact of exposing oneself to the sun’s mutagenic effects is likely more significant than the advantageous effect of acquiring adequate vitamin D in the bloodstream.
Required dose of Vitamin D
In the United States, the current daily recommendations for vitamin D include:
- birth to 12 months: 10 micrograms (400 international units)
- children 1–13 years: 15 mcg (600 IU)
- teens 14–18 years: 15 mcg (600 IU)
- adults 19–70 years: 15 mcg (600 IU)
- adults 71 years and older: 20 mcg (800 IU)
- pregnant and nursing people: 15 mcg (600 IU)
Dr.Harvima stated that ‘Eventhough vitamin D supplementation alone is unlikely an effective medication to treat metastatic melanoma, many people may get benefitted ateast to reduce the risk. And she further added that different countries will have variations in recommended daily dosage and they should follow their country’s national guidelines’
Research findings
The research that was conducted in collaboration with University of Eastern Finland and Kuopio University Hospital arrived at a conclusion after examining patient’s background information, medical history and skin conditions classifying them into three cancer risk categories as high risk, moderate risk and low risk. Then, the patients were further classified based on their oral consumption of vitamin D supplements, whether they are regular users, occassional users and nonusers.
And also according to the melanoma research which was described earlier, high circulating vitamin D concentration has been found to be related to less progression of melanoma.
And they came to a conclusion that the skin cancer risk was less for regular users of vitamin D than non users meanwhile it was less even for occassional users compared to non users.
Key takeaway
Overall, while some studies suggest that vitamin D supplements may be beneficial for reducing skin cancer risk, more research is needed to fully understand this relationship and to determine the optimal dosage and duration of supplementation. In the meantime, it’s important to continue practicing sun safety measures, such as wearing protective clothing, seeking shade during peak UV hours, and using sunscreen with a high SPF.
As something is better than nothing, taking vitamin D supplements of appropriate dosage prescribed by a doctor would definitely be a better choice to prevent from the risk of skin cancers!
Disclaimer
The information provided in this article is for educational and informational purposes only and is not intended to be a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the advice of a qualified healthcare provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition. The use of vitamin D supplements to prevent or reduce the risk of skin cancer should be discussed with a healthcare professional, and the optimal dose for individual needs should be determined by a qualified healthcare provider.
References
- Holick MF. Vitamin D status: measurement, interpretation, and clinical application. Ann Epidemiol. 2009 [cited 2023 Feb 25];19(2):73–8. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.annepidem.2007.12.001
- Vitamin D. Nih.gov. [cited 2023 Feb 25]. https://ods.od.nih.gov/factsheets/VitaminD-Consumer/
- Davenport L. Regular vitamin D supplements may lower melanoma risk. Medscape. 2023 [cited 2023 Feb 25]. https://ods.od.nih.gov/factsheets/VitaminD-Consumer/
- Kanasuo E, Siiskonen H, Haimakainen S, Komulainen J, Harvima IT. Regular use of vitamin D supplement is associated with fewer melanoma cases compared to non-use: a cross-sectional study in 498 adult subjects at risk of skin cancers. Melanoma Res. 2023 [cited 2023 Feb 25];33(2):126–35. https://journals.lww.com/melanomaresearch/Abstract/9900/Regular_use_of_vitamin_D_supplement_is_associated.51.aspx
Ask a Dermatologist Now
Anonymous, fast and secure!

The Specialist doctor from the University Hospital in Gothenburg, alumnus UC Berkeley. My doctoral dissertation is about Digital Health and I have published 5 scientific articles in teledermatology and artificial intelligence and others.