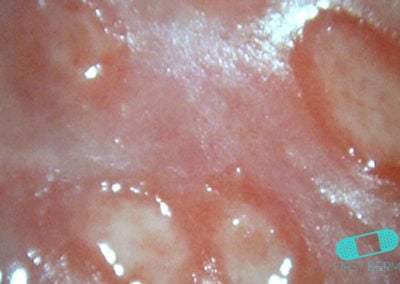
Genital Sores
Medically reviewed by The Dermatologists and written by Dr. Alexander Börve
- Requires medical diagnosis
- Symptoms: Small bumps, blisters or patches
- Color: Typically red, white or brown
- Location: In or around the vagina for females
- Treatment: Antibiotics, antiviral medications, corticosteroids, pain relievers, hydrocortisone or other anti-itch drugs
Genital sores can be a symptom of many skin conditions, but most often they are signs of sexually transmitted infections (STIs).
STIs affect all populations, but young women are especially at risk for developing serious long-term health complications as a result of untreated infections. They can be spread through oral, vaginal, anal sex or the sharing of sex toys.
Some other non-STI-related causes of genital sores are vulvovaginitis, contact dermatitis and atopic dermatitis. Skin cancer or cysts can cause sores in the genital areas as well.
Get peace of mind and get a home STD Lab Test today, sent discretely.
Symptoms
Genital sores appear as bumps and lesions in or around the vagina for females.
These lesions are small, red or flesh-colored bumps and blisters. They can become crusty or grow in size. Some may cause itching, tenderness, discomfort when urinating or during sexual intercourse. You may also experience persistent pain at the site or in the pelvis. Bleeding is not uncommon. While you may see abnormal, foul-smelling discharge, some STIs are asymptomatic and painless.
Examples of STIs that can cause female genital sores include:
- Genital herpes
- Genital warts
- Chancroid (a bacterial disease)
- Syphilis
- Molluscum contagiosum
White, red or brown patches on the vulva may lead to vulgar dysplasia (cancer of the vulva).
Get peace of mind and get a home STD Lab Test today, sent discretely.
What can I do?
The best way to prevent genital sores is to practice safe and protected sex. Also, you can try to avoid known irritants, such as abrasive soaps or strong fragrances.
Do not have any type of sexual activity until your healthcare provider determines that you can no longer spread a STI to your sexual partners.
Should I seek medical care?
You should contact a healthcare provider if you suspect that you have a STI. A physician or board-certified dermatologist can usually determine the cause and prevent potentially dangerous medical complications.
If the sores are caused by a STI your sexual partner may need to be treated as well. It is important to protect your health and also avoid spreading an STI to sexual partners.
Get peace of mind and get a home STD Lab Test today, sent discretely.
Treatment
Physical examination, pelvic exam and laboratory tests can test the presence of bacteria and help determine the cause. After identifying the cause, your healthcare provider can prescribe topical and oral medications accordingly. Sometimes, no treatment is necessary, such as in the case of noncancerous cyst.
Commonly used medications for genital sores include antibiotics, antiviral medications, corticosteroids, pain relievers, hydrocortisone and other anti-itch drugs.
Get peace of mind and get a home STD Lab Test today, sent discretely.
Source:
Kristeen Moore. Medically Reviewed by Steven Kim, MD. Female Genital Sores. Available at: http://www.healthline.com/health/genital-sores-female#Treatment6
U.S. National Library of Medicine. Genital Sores – female. Available at: https://www.nlm.nih.gov/medlineplus/ency/article/003222.htm
Image from Healthline. First Derm watermark added. Accessed July 8, 2016. Available at: http://www.healthline.com/health/genital-sores-female#Diagnosis4
Ask a Dermatologist
Anonymous, fast and secure!

The Specialist doctor from the University Hospital in Gothenburg, alumnus UC Berkeley. My doctoral dissertation is about Digital Health and I have published 5 scientific articles in teledermatology and artificial intelligence and others.